Here and there some tension and hardening. Everyone knows the feeling – so, off to the next massage or physiotherapy. But let me say, there is an easier way: Try some of the fascia training exercises and experience what you can do for your health and different areas of your body. It will save time and money.
Fascias are a part of our connective tissue. They run through our entire body continuously from head to toe. They connect muscles, bones, nerves, blood vessels and organs by ‘weaving’ them together in a network of fibres. Without fascias, organs and bones would loosely hang around in the body. The connective tissue-like fibres are involved in all movements and build the foundation of our physical health and performance.
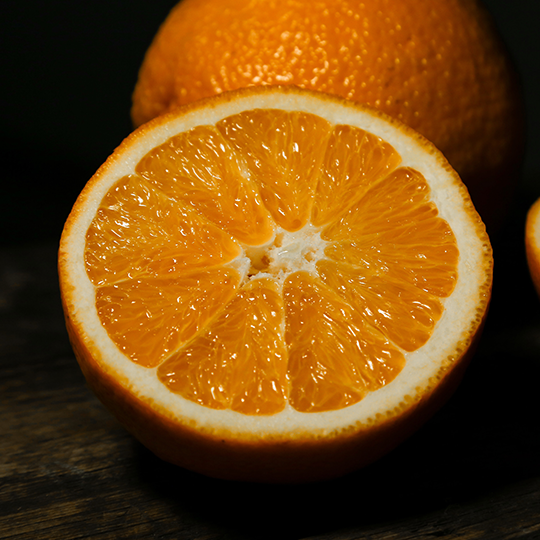
To get a better idea of a fascia, think of an orange. Fascias are similar to the skin inside, holding everything together and thus determinining the overall structure.


Fascial training is not about “faster, higher, further”, but about variety and continuity. Therefore, it is better to train regularly and moderately than rarely and intensively!
Influence of the fascia
Nutrition and stress can also have an influence on the fascias. However, movement is the biggest factor influencing whether my fascias are healthy or causing pain!
Long-term stress or excessive and negative physical strain lead to stiffness and matting of fascial structures. Lymphatic vessels, which among other things transport the blood clotting factor fibrinogen, run through the fascias. Muscle tension or lack of exercise can lead to lymphostasis.
The fibrinogen is broken down into fibrin, an “adhesive” that glues together the surrounding fascial tissue. The consequences: the affected muscles lose flexibility and mobility, nerves are squeezed in the “glued” tissue area. In the long-term tension, pain, or even chronic back problems can occur.
Influence
Nutrition, stress and above all exercise
Physiology
Fascias consist mainly of water and collagen
Consequences
the fascias lose flexibility when there is a lack of movement
How can you prevent this?
Probably you’ve already guessed it correctly. Sufficient movement is the key. But it is not only about sports activities, but rather about regular and moderate movement. This can be a short and active break at work or a quick walk. The more we move the fascias, the easier it is for them to maintain their flexibility and functionality.
Especially in the office or home office, we quickly fall into unfavorable postures and do not even notice how long we remain in these positions.
You can prevent this unhealthy habit by creating reminders in your everyday life. This can help to establish new habits integrating regular movement. If you need support and more tips on how to tackle this, take a look at content room FASCIA TRAINING. You’ll find many useful tips and suggestions for an active lifestyle, which in turn will help your fascias to stay smooth and healthy.
Analysis
regular moderate exercise
check habits
poor body position
Develop a routine
Integrate movement
References
- Faszientraining. Theorie und Praxis zum Aufbau eines geschmeidig-kraftvollen Bindegewebes. Schleip, R. & Müller, D. (2011)
- Foam-Rolling in sport and therapy – Potential benefits and risks. Part 2. Freiwald, J. et al. (2016)
- Grundlagenwissen Faszien. Hodeck, K. (2015)
- Funktionelles Faszientraining mit der Blackroll. Lutz Graumann, Marcel Andrä, Torsten Pfitzer. Riva Verlag: 7. Auflage 2018
- The effects of self-myofascial release using a foam roll or roller massager on joint range of motion, muscle recovery, and performance: a systematic review. Scott W Cheatham , Morey J Kolber, Matt Cain, Matt Lee (2015)
- Acute Effects of Lateral Thigh Foam Rolling on Arterial Tissue Perfusion Determined by Spectral Doppler and Power Doppler Ultrasound. Thilo Hotfiel et al. (2017)